Both fog and clouds are formed when water vapor condenses or freezes to form tiny droplets or crystals in the air. So why are they two different things?
Fog forms only at low altitudes.
Clouds can form at many different altitudes. They can be as high as 12 miles above sea level or as low as the ground. Fog is a kind of cloud that touches the ground. Fog forms when the air near the ground cools enough to turn its water vapor into liquid water or ice.
There are many different types of fog, too. Ice fog forms when the air near the ground is cold enough to turn the water in fog into ice crystals. Ice fog forms only at extremely cold temperatures. Ice fog is common in parts of Alaska and Canada.
Another kind of fog is freezing fog. Ice crystals form in the air when it’s cold enough and particles like dust or smoke in the air provide a “seed” for the ice crystal to form around. Sometimes it is cold enough, but the air does not have any particles. In this case, water in the air becomes “supercooled.” This supercooled water is a liquid, but it is colder than the freezing point (32ºF). When it comes into contact with cold surfaces such as roads and sidewalks, it instantly forms a dangerous icy layer.
One of the most troubling kinds of fog is called “super fog.” Super fog forms when smoke from wildfires and water vapor come together to form an extremely dense fog. The smoke provides particles for the water vapor to condense around. This combination of smoke and water vapor is a dangerous one. A super fog is so dense that you would not be able to see your own hand in front of your face. Superfogs create very hazardous driving conditions.

Fog and smoke from a brush fire combined to make a super fog, resulting in this massive car accident in Florida in 2008. Photo used with permission of Orlando Sentinel, Copyright 2008.
Fog can be a big problem for humans, especially when we have to drive or fly through it.
How can we prepare for fog?
Thousands of driving accidents happen each year because of fog. Fog also creates trouble for air travelers. Foggy conditions create dangerous flying conditions and can delay or cancel flights.
Pilots and drivers can get some help from space, though. Two types of satellites from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) monitor fog from high in the sky. The first is called a geostationary satellite. These satellites orbit Earth in the same exact time that it takes for Earth to make a full rotation. Orbiting Earth in such a way allows the satellite to hover over one location, providing a bird's eye view.
The second kind is a polar satellite. The orbits of these satellites cross over each of the poles. Earth rotates under these satellites as they make the trip from pole to pole. Because the Earth rotates while the satellite makes its orbit, it is able to see nearly every part of Earth’s surface.
NOAA is developing a new generation of geostationary and polar satellites. These satellites will be able to take very high-resolution photos of clouds and fogs. This information can tell pilots or drivers where to expect fog, and can help save lives.
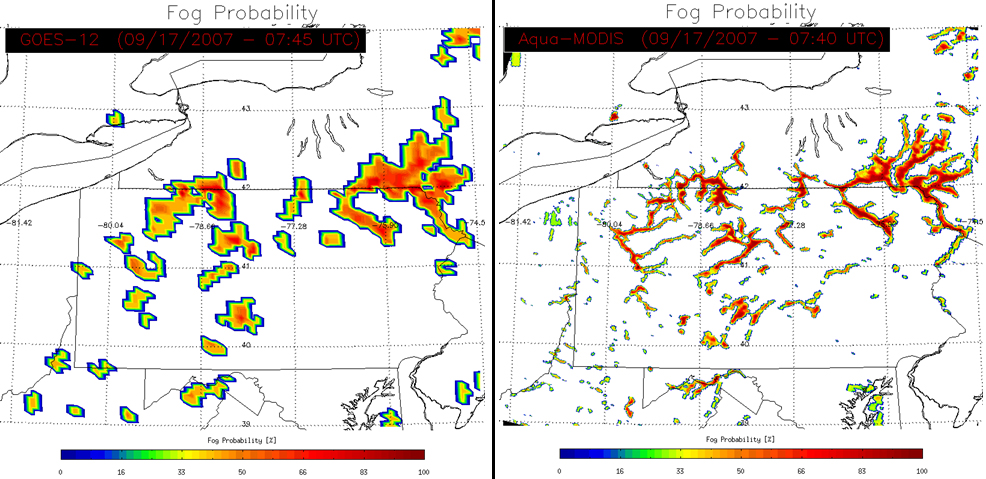
Satellite data can be used to predict the likelihood of fog forming. Current geostationary and polar satellites, however, are capable only of producing a low-resolution picture, like the image on the left. The next generation of geostationary and polar satellites, the GOES-R series and JPSS, will be able to produce a much more detailed and accurate image, like the image on the right.





